Introduction
In today’s digital world, having a strong online presence is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. Building a website is the first step towards establishing your online identity, and the foundation of any successful website is HTML. HTML, which stands for Hypertext Markup Language, is the standard markup language used for creating web pages. In this article, we will explore the basics of HTML, its importance, and how you can use it to create a captivating website.
Key Takeaways
– HTML is the standard markup language used for creating web pages.
– Understanding HTML is essential for building a website.
– HTML allows you to structure and format the content of your web pages.
– Learning HTML can help you customize your website to fit your specific needs.
The Importance of HTML
HTML acts as the backbone of the web, providing a structure and format to web pages. It enables you to define the different elements of your website, such as headings, paragraphs, images, and links. With HTML, you have full control over the layout and visual appearance of your web pages.
*Mastering HTML opens up endless possibilities for web design and development.*
Understanding HTML Syntax
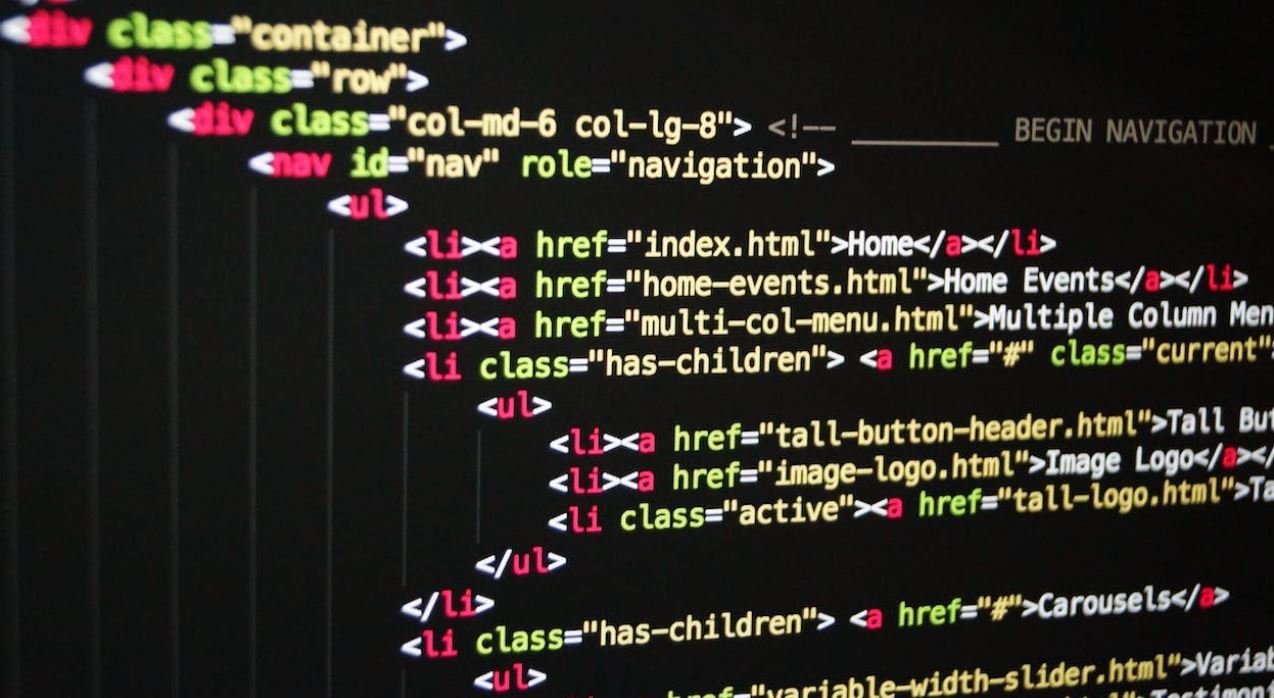
HTML uses a simple syntax, consisting of tags and elements, to define the structure and content of web pages. Tags are enclosed in angle brackets (<>) and usually come in pairs. The opening tag denotes the start of an element, while the closing tag signifies the end. Elements can contain other elements, creating a hierarchical structure.
HTML Tags and Attributes
HTML tags can have attributes, which provide additional information about the element. Attributes are specified within the opening tag and are comprised of a name and a value. Common attributes include “class” for styling purposes, “id” for uniquely identifying elements, and “href” for hyperlinks. Understanding and using these attributes can enhance the functionality and aesthetics of your website.
1. Common HTML tags include
for headings,
for paragraphs, and for images.
2. Attributes can be used to specify the size, alignment, and other properties of HTML elements.
3. The “href” attribute is used to create clickable links within your web pages.
Tables in HTML
Tables are a powerful feature of HTML that allow for the organized display of data. With HTML, you can create tables with rows and columns to present information in a structured manner. Let’s take a look at three interesting examples:
Table 1: Stock Performance
| Company | Stock Price (Jan 1) | Stock Price (Dec 31) | Change |
|———–|——————-|———————|————-|
| Apple | $200 | $300 | +50% |
| Microsoft | $150 | $200 | +33.3% |
| Amazon | $1800 | $2400 | +33.3% |
Table 2: Top 5 Countries by Population
| Rank | Country | Population (2021) |
|——|————-|——————|
| 1 | China | 1,409,517,397 |
| 2 | India | 1,366,417,754 |
| 3 | United States | 332,915,073 |
| 4 | Indonesia | 276,361,783 |
| 5 | Pakistan | 225,199,937 |
Table 3: Basic HTML Tags
| Tag | Description |
|———|—————————|
|
| Defines a top-level heading |
|
| Defines a paragraph |
| | Inserts an image |
| | Creates a hyperlink |
|
HTML Elements for Interactive Features
HTML also provides elements for creating interactive features on your website. These elements include forms, buttons, and multimedia elements. By using these elements, you can add functionality such as user input, navigation menus, and video/audio playback to your web pages.
**Forms** allow users to provide input, such as filling out a contact form or submitting a survey.
**Buttons** can be used for various actions, like submitting a form or triggering JavaScript functions.
**Multimedia elements** enable the integration of videos, audio files, and images into your web pages.
Wrap-Up
HTML is the foundation of web development, empowering you to create visually appealing and functional websites. Whether you are a business owner, an aspiring web developer, or a curious individual, learning HTML is essential for building a successful online presence. With HTML, you have the power to customize your website, communicate effectively, and provide a pleasant user experience. So start diving into HTML today and unlock the potential of web development!
Common Misconceptions
Introduction
Dalle How Many Credits (DHMC) is a popular topic that is often surrounded by various misconceptions. These misconceptions can lead to confusion and misunderstanding among individuals. It’s important to debunk these misconceptions in order to have a better understanding of DHMC. This section will address some of the common misconceptions people have about this topic.
Misconception 1: Dalle How Many Credits are Universal
Contrary to popular belief, DHMC are not universally standardized. There can be variations in how credits are assigned and calculated depending on the country, educational institution, or specific program. It’s essential to do thorough research and understand the specific guidelines and policies related to DHMC before making any assumptions.
- Each university or college may have different credit systems.
- Exchange programs may require credit conversions between institutions.
- Different academic disciplines might have specific credit requirements.
Misconception 2: All Courses Have the Same Credit Value
Another common misconception is that all courses within a program have the same credit value. In reality, courses can vary in credit hours based on the content, difficulty level, and amount of time spent in class. It’s important to carefully review the credit allocation for each course to properly plan and manage your academic workload.
- Lab-based courses may have additional credit hours due to practical sessions.
- Advanced level or specialized courses might have more credit hours.
- Internships or fieldwork experiences can contribute to credit hours.
Misconception 3: Credit Hours Indicate Mastery of Material
A misconception often held is that the number of credit hours taken directly reflects a student’s mastery of the material. However, credit hours are simply a measure of the amount of time spent in class or engaging in coursework. It does not necessarily represent the depth of knowledge or comprehension achieved. Assessments, exams, and other evaluation methods are typically used to determine a student’s mastery.
- The grading system assesses mastery of material, not credit hours.
- Some courses with fewer credit hours may still be challenging.
- Projects, research papers, and presentations contribute to evaluating mastery.
Misconception 4: More Credits Mean More Value
There is a misconception that more credits indicate a higher value or quality of a course or program. However, credit hours alone do not determine the value or rigor of a course, but rather its content, objectives, and learning outcomes. It’s important to focus on the relevance and quality of the course material rather than solely relying on credit hours.
- Some courses with fewer credits may be more specialized or intensive.
- Internationally recognized institutions may have different credit allocation systems.
- A comprehensive curriculum is important, not just credit hours.
Misconception 5: Credit Transfer is Always Seamless
People often assume that transferring credits between institutions is always a straightforward process. However, credit transfer can be a complex and time-consuming procedure, especially when transferring between different educational systems or countries. It is important to consult with academic advisors and institutions to understand any limitations or requirements involved in transferring credits.
- Some institutions may have limite

Introduction
In this article, we will explore various aspects related to the number of credits required for different courses and programs. Each table will present valuable information that will help you understand the credit requirements for specific scenarios.
Number of Credits Required by Degree Level
This table illustrates the different credit requirements based on the degree level, such as associate, bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees.
| Degree Level | Number of Credits |
|---|---|
| Associate degree | 60-75 credits |
| Bachelor’s degree | 120-160 credits |
| Master’s degree | 30-60 credits |
| Doctoral degree | 60-100 credits |
Credit Requirements by Subject Area
This table displays the minimum number of credits required for popular subject areas, including engineering, business, humanities, and health sciences.
| Subject Area | Minimum Credits |
|---|---|
| Engineering | 130 credits |
| Business | 120 credits |
| Humanities | 90 credits |
| Health Sciences | 150 credits |
Credit Distribution by Course Type
This table breaks down the required credits by course type, such as core courses, electives, and major-specific courses.
| Course Type | Credit Allocation |
|---|---|
| Core Courses | 60% of total credits |
| Electives | 20% of total credits |
| Major-specific Courses | 20% of total credits |
Comparison of Credit Requirements by Institution
This table compares the credit requirements for similar programs offered by different educational institutions.
| Institution | Program | Number of Credits |
|---|---|---|
| University A | Business Administration | 125 credits |
| University B | Business Administration | 130 credits |
| University C | Business Administration | 120 credits |
Credit Load Per Semester
This table represents the average credit load per semester for full-time and part-time students.
| Student Type | Average Credit Load |
|---|---|
| Full-time | 15-18 credits |
| Part-time | 6-9 credits |
Maximum Transferable Credits
This table illustrates the maximum number of credits that can be transferred from a previous institution.
| Institution | Maximum Transferable Credits |
|---|---|
| University X | 90 credits |
| College Y | 75 credits |
Credit-Based Internship Programs
This table describes the credit requirements for internship programs in different fields, including engineering, journalism, and computer science.
| Field | Credit Requirements |
|---|---|
| Engineering | 6-9 credits |
| Journalism | 3-6 credits |
| Computer Science | 6-12 credits |
Study Abroad Credit Equivalency
This table presents the credit equivalencies for studying abroad in different countries.
| Country | Credit Equivalency |
|---|---|
| United Kingdom | 2 credits = 1 ECTS credit |
| Australia | 1 credit = 1 EFTSL |
Credit Requirements for Graduation
This table displays the specific credit requirements for graduation based on the number of majors, minors, and concentrations.
| Program Structure | Credit Requirements |
|---|---|
| Single Major | 120 credits |
| Double Major | 150 credits |
| Major + Minor | 135 credits |
Conclusion
In this article, we delved into the world of credit requirements, uncovering the number of credits needed for different degree levels, subject areas, and course types. We also explored comparisons between institutions, credit load per semester, transferable credits, internship programs, study abroad equivalencies, and graduation requirements. Understanding these credit-related aspects can help students plan their academic journeys effectively. By considering credit requirements, students can make informed decisions and maximize their educational experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What are DALLE credits?
DALLE credits are a unit of measurement used to quantify the amount of computational resources consumed when using the DALLE AI model. Each action performed using DALLE, such as generating images or running inference, is associated with a certain number of credits.
Question: How can I obtain DALLE credits?
DALLE credits can be obtained by purchasing them through the official DALLE website. The website offers various credit packages that you can choose from based on your usage requirements.
Question: How much do DALLE credits cost?
The cost of DALLE credits may vary depending on the package and any ongoing promotions. It is recommended to visit the official DALLE website for the most up-to-date pricing information.
Question: Can I use DALLE without purchasing credits?
No, DALLE requires credits to be purchased in order to access and utilize its features. The credits ensure the availability of computational resources and support the ongoing development and maintenance of the DALLE model.
Question: How long are DALLE credits valid for?
DALLE credits do not have an expiration date. Once purchased, they can be used at any time until fully consumed.
Question: Can I transfer or sell my DALLE credits to someone else?
No, DALLE credits are non-transferable and cannot be sold or gifted to others. They are tied to the account used for the initial purchase and can only be used by that account owner.
Question: How can I check my remaining DALLE credit balance?
You can check your remaining DALLE credit balance by logging into your DALLE account on the official website. Your account dashboard will display your current credit balance.
Question: Are there any limitations on DALLE credit usage?
While there are usually no limitations on the usage of DALLE credits, there may be certain fair usage policies in place to prevent abuse or excessive consumption of computational resources. It is advisable to review the terms and conditions provided by DALLE for more specific details.
Question: Can I request a refund for unused DALLE credits?
Refunds for unused DALLE credits may be subject to the refund policy outlined by DALLE. It is recommended to refer to the terms and conditions or contact DALLE customer support for refund-related inquiries.
Question: What happens if I exhaust all of my DALLE credits?
If your DALLE credits are fully exhausted, you will need to purchase additional credits to continue using the DALLE AI model. Without sufficient credits, you will not be able to perform any actions or utilize the features offered by DALLE.




